GO实现BTC-V3-存储
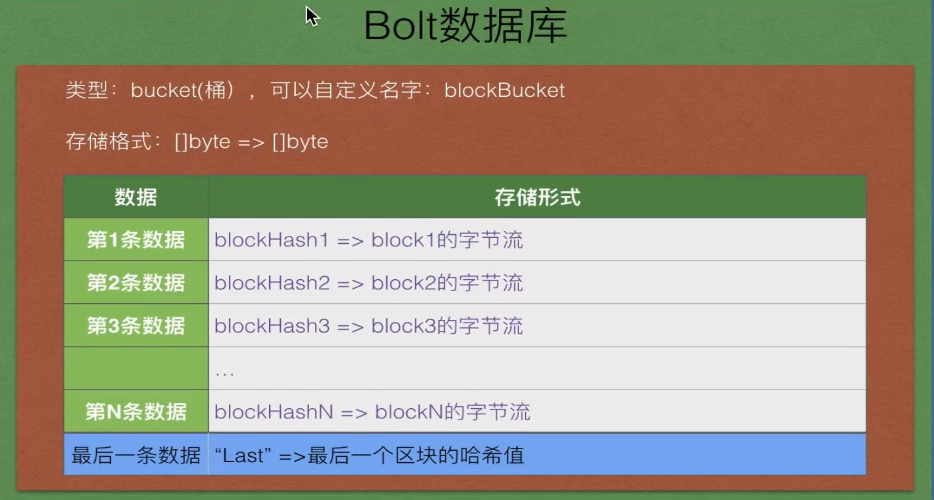
分析bolt存储区块的格式
key一定唯一:
把所有的区块都写到一个bucket中:key-> value : []byte->[]byte :
在bucket存储两种数据:
1. 区块,区块的哈希值作为key,区块的字节流作为value
block.Hash -> block.toBytes()
2. 最后一个区块的哈希值
key使用固定的字符串:[]byte(“lastHashKey”), value 就是最后一个区块的哈希
添加一个新区块要做两件事情:
1、添加区块
2、更新”lastHashKey“ 这个key对应的值,这个值就是最后一个区块的哈希值,用于新区块的创建添加。
改写区块链,获取区块链实例
//实现创建区块链的方法
func NewBlockChain() *BlockChain {
//功能分析:
//1. 获得数据库的句柄,打开数据库,读写数据
db, err := bolt.Open("blockChain.db", 0600, nil)
//向数据库中写入数据
//从数据库中读取数据
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
defer db.Close()
var tail []byte
db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
b := tx.Bucket([]byte("blockBucket"))
if b == nil {
//如果b1为空,说明名字为"buckeName1"这个桶不存在,我们需要创建之
fmt.Printf("bucket不存在,准备创建!\n")
b, err = tx.CreateBucket([]byte("blockBucket"))
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
//抽屉准备完毕,开始添加创世块
genesisBlock := NewBlock(genesisInfo, []byte{})
b.Put(genesisBlock.Hash, genesisBlock.toBytes() /*将区块序列化,转成字节流*/)
b.Put([]byte("lastHashKey"), genesisBlock.Hash)
tail = genesisBlock.Hash
} else {
tail = b.Get([]byte("lastHashKey"))
}
return nil
})
return &BlockChain{db, tail}
}
编码解码区块
//序列化, 将区块转换成字节流
func (block *Block) Serialize() []byte {
var buffer bytes.Buffer
//定义编码器
encoder := gob.NewEncoder(&buffer)
//编码器对结构进行编码,一定要进行校验
err := encoder.Encode(block)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
return buffer.Bytes()
}
func Deserialize(data []byte) *Block {
fmt.Printf("解码传入的数据: %x\n", data)
var block Block
//创建解码器
decoder := gob.NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(data))
err := decoder.Decode(&block)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
return &block
}
更新AddBlcok
//添加区块
func (bc *BlockChain) AddBlock(data string) {
//1. 创建一个区块
bc.db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
b := tx.Bucket([]byte("blockBucket"))
if b == nil {
fmt.Printf("bucket不存在,请检查!\n")
os.Exit(1)
}
block := NewBlock(data, bc.tail)
b.Put(block.Hash, block.Serialize() /*将区块序列化,转成字节流*/)
b.Put([]byte("lastHashKey"), block.Hash)
bc.tail = block.Hash
return nil
})
}
定义迭代器,创建迭代器
//定义一个区块链的迭代器,包含db,current
type BlockChainIterator struct {
db *bolt.DB
current []byte //当前所指向区块的哈希值
}
//创建迭代器,使用bc进行初始化
func (bc *BlockChain) NewIterator() *BlockChainIterator {
return &BlockChainIterator{bc.db, bc.tail}
}
Next函数实现
func (it *BlockChainIterator) Next() *Block {
var block Block
it.db.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error {
b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blockBucketName))
if b == nil {
fmt.Printf("bucket不存在,请检查!\n")
os.Exit(1)
}
//真正的读取数据
blockInfo /*block的字节流*/ := b.Get(it.current)
block = *Deserialize(blockInfo)
it.current = block.PrevBlockHash
return nil
})
return &block
}
使用迭代器更新main函数
package main
import (
"fmt"
//"time"
"time"
"bytes"
)
func main() {
fmt.Printf("helloworld\n")
//block := NewBlock(genesisInfo, []byte{0x0000000000000000})
bc := NewBlockChain()
defer bc.db.Close()
bc.AddBlock("hello itcast!!!")
it := bc.NewIterator()
for {
block := it.Next()
fmt.Printf("++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++\n")
fmt.Printf("Version : %d\n", block.Version)
fmt.Printf("PrevBlockHash : %x\n", block.PrevBlockHash)
fmt.Printf("MerKleRoot : %x\n", block.MerKleRoot)
timeFormat := time.Unix(int64(block.TimeStamp), 0).Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05")
fmt.Printf("TimeStamp : %s\n", timeFormat)
fmt.Printf("Difficulity : %d\n", block.Difficulity)
fmt.Printf("Nonce : %d\n", block.Nonce)
fmt.Printf("Hash : %x\n", block.Hash)
fmt.Printf("Data : %s\n", block.Data)
pow := NewProofOfWork(block)
fmt.Printf("IsValid: %v\n", pow.IsValid())
if bytes.Equal(block.PrevBlockHash, []byte{}) {
fmt.Printf("区块链遍历结束!\n")
break
}
}
}
命令行demo
package main
import (
"os"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
cmds := os.Args
for i, cmd := range cmds {
fmt.Printf("cmd[%d] : %s\n", i, cmd)
}
}
使用命令行分析
1. 所有的支配动作交给命令行来做
2. 主函数只需要调用命令行结构即可
3. 根据输入的不同命令,命令行做相应动作
1. addBlock
2. printChain
CLI : command line的缩写
type CLI struct {
bc *BlockChain
}
添加区块的时候: bc.addBlock(data), data 通过os.Args拿回来
打印区块链时候:遍历区块链,不需要外部输入数据
定义CLI结构, Run方法框架搭建
const Usage = `
./blockchain addBlock "xxxxxx" 添加数据到区块链
./blockchain printChain 打印区块链
`
type CLI struct {
bc *BlockChain
}
//给CLI提供一个方法,进行命令解析,从而执行调度
func (cli *CLI) Run() {
cmds := os.Args
if len(cmds) < 2 {
fmt.Printf(Usage)
os.Exit(1)
}
switch cmds[1] {
case "addBlock":
fmt.Printf("添加区块命令被调用, 数据:%s\n", cmds[2])
case "printChain":
fmt.Printf("打印区块链命令被调用\n")
default:
fmt.Printf("无效的命令,请检查\n")
fmt.Printf(Usage)
}
//添加区块的时候: bc.addBlock(data), data 通过os.Args拿回来
//打印区块链时候:遍历区块链,不需要外部输入数据
}
改写main函数
package main
func main() {
bc := NewBlockChain()
defer bc.db.Close()
cli := CLI{bc}
cli.Run()
}
更新Run函数
//给CLI提供一个方法,进行命令解析,从而执行调度
func (cli *CLI) Run() {
cmds := os.Args
if len(cmds) < 2 {
fmt.Printf(Usage)
os.Exit(1)
}
switch cmds[1] {
case "addBlock":
fmt.Printf("添加区块命令被调用, 数据:%s\n", cmds[2])
data := cmds[2]
cli.AddBlock(data)
case "printChain":
fmt.Printf("打印区块链命令被调用\n")
cli.PrintChain()
default:
fmt.Printf("无效的命令,请检查\n")
fmt.Printf(Usage)
}
//添加区块的时候: bc.addBlock(data), data 通过os.Args拿回来
//打印区块链时候:遍历区块链,不需要外部输入数据
}
添加commands.go 具体实现命令的文件
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"bytes"
)
//实现具体的命令
func (cli *CLI) AddBlock(data string) {
cli.bc.AddBlock(data)
fmt.Printf("添加区块成功!\n")
}
func (cli *CLI) PrintChain() {
it := cli.bc.NewIterator()
for {
block := it.Next()
fmt.Printf("++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++\n")
fmt.Printf("Version : %d\n", block.Version)
fmt.Printf("PrevBlockHash : %x\n", block.PrevBlockHash)
fmt.Printf("MerKleRoot : %x\n", block.MerKleRoot)
timeFormat := time.Unix(int64(block.TimeStamp), 0).Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05")
fmt.Printf("TimeStamp : %s\n", timeFormat)
fmt.Printf("Difficulity : %d\n", block.Difficulity)
fmt.Printf("Nonce : %d\n", block.Nonce)
fmt.Printf("Hash : %x\n", block.Hash)
fmt.Printf("Data : %s\n", block.Data)
pow := NewProofOfWork(block)
fmt.Printf("IsValid: %v\n", pow.IsValid())
if bytes.Equal(block.PrevBlockHash, []byte{}) {
fmt.Printf("区块链遍历结束!\n")
break
}
}
}